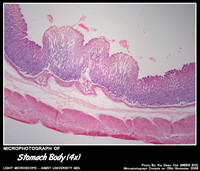
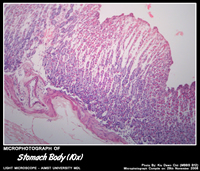
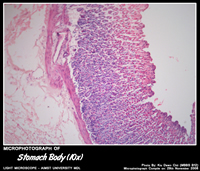
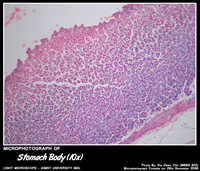
STOMACH BODY
Histology of Stomach
- Mucosa – gastric glands, two or three layers of muscularis mucosae & an intervening lamina propria.
- Smooth muscle of the muscularis externa is arrarnged in three layers – outer longitudinal, middle circular, and inner circular.
- submucosa of the stomach is made up of loose connective tissue. It has a rich vascular and lymphatic net work.
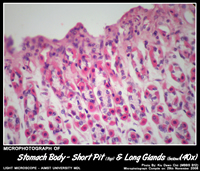
- Slight variations in four major regions – cardia, fundus, body and pylorus.
- Serosa composed of a thin loose connective tissue covered by a smooth wet, simple squamous epithelium.
Cells of Stomach Gland
- Mucous neck cells (columnar) - produce a soluble mucus that lubricates the chyme, reducing friction as it moves along the digestive tract.
- Regenerative (stem) cells (columnar) - they replace all the specialized cells lining the fundic glands.
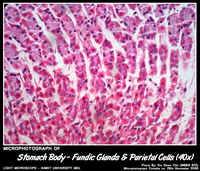
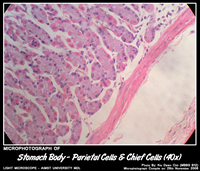
- Parietal cells (eosinophilic cytoplasm,round basally located nuclei) - manufacture hydrochloric acid and gastric intrinsic factor.
- Chief (zymogenic) cells (columnar, basophilic cytoplasm,basally situated nuclei) - apically situated secretory granules containing the proenzyme pepsinogen (rennin and gastric lipase). Most of these cells are in the base of the fundic glands.
Histology of Fundus & Body of Stomach
- Gastric glands known as fundic glands – shallow pits(1/3rd of the mucosal depth) and long glands.
- Fundic glands contain abundant – parietal and chief cells.
Histology of Pyloric Region of Stomach
- Glands are known as Pyloric glands.
- Deep pits and short glands.
- Large pale staining mucus secreting cells with basal nuclei predominate, parietal cells rare.
Click to enlarge